- Thumbnail
-
- Resources
- brh.co.jp/
- Author
- JT Biohistory Research Hall
- Printed File Format
- Page(s)
- 2
- Part(s)
- 17
- Instruction Format
Sponsored:
Sponsored 2:
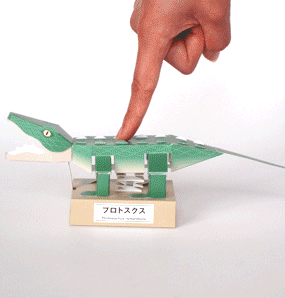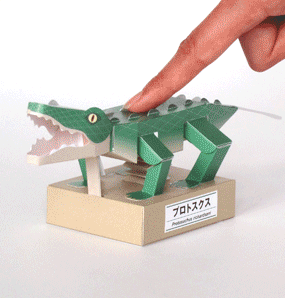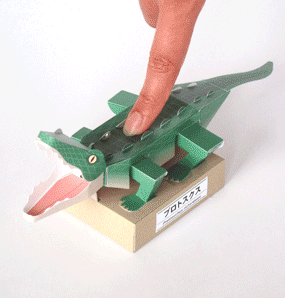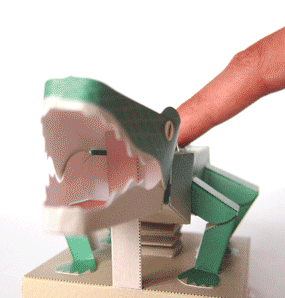
Protosuchus Richardsoni automata papercraft
Before the heyday of dinosaurs, crocodiles were vertebrates that prospered on land, adapting widely to the water's edge and evolving into various shapes.
Protosuchus is an extinct genus of carnivorous crocodylomorph from the Early Jurassic. The name Protosuchus means "first crocodile", and is among the earliest animals that resemble crocodilians. Protosuchus was about 1 metre (3.3 ft) in length and about 40 kilograms (88 lb) in weight.
As an early crocodilian relative, its skull featured more crocodilian characteristics than its earlier ancestors; it had short jaws that broadened out at the base of the skull, providing a large surface to which its jaw muscles could attach. This increased the maximum gape of the animal's mouth and the force with which the jaws could be closed. The dentition of the animal also resembled modern crocodiles, including the teeth in the lower jaw that fitted into notches on either side of the upper jaw when the mouth was closed. It also possessed a powerful tail which later developed into a propulsion mechanism through water in its descendants.
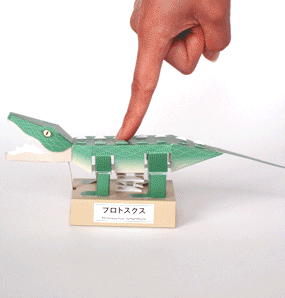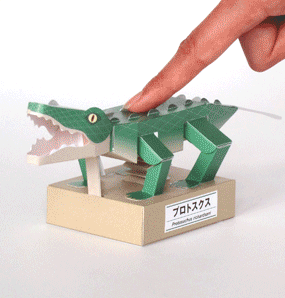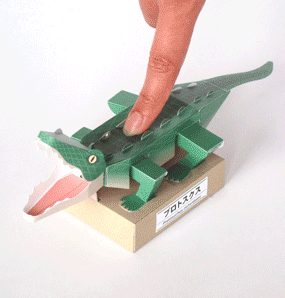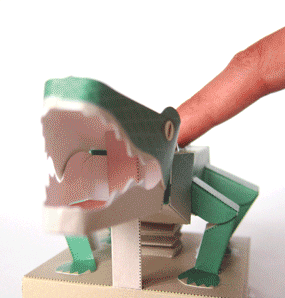
The body was covered and reinforced by osteoderms in a double row along the back and covering the bottom of the body and the entire tail. It was an unusual quadrupedal reptile whose legs were columnar, with the rear legs longer than the front legs. Its five toes were clawed and it is believed that they were good runners and good swimmers.
Protosuchus is an extinct genus of carnivorous crocodylomorph from the Early Jurassic. The name Protosuchus means "first crocodile", and is among the earliest animals that resemble crocodilians. Protosuchus was about 1 metre (3.3 ft) in length and about 40 kilograms (88 lb) in weight.
As an early crocodilian relative, its skull featured more crocodilian characteristics than its earlier ancestors; it had short jaws that broadened out at the base of the skull, providing a large surface to which its jaw muscles could attach. This increased the maximum gape of the animal's mouth and the force with which the jaws could be closed. The dentition of the animal also resembled modern crocodiles, including the teeth in the lower jaw that fitted into notches on either side of the upper jaw when the mouth was closed. It also possessed a powerful tail which later developed into a propulsion mechanism through water in its descendants.

The body was covered and reinforced by osteoderms in a double row along the back and covering the bottom of the body and the entire tail. It was an unusual quadrupedal reptile whose legs were columnar, with the rear legs longer than the front legs. Its five toes were clawed and it is believed that they were good runners and good swimmers.
Sponsored: Google Advertising
