- Thumbnail
-
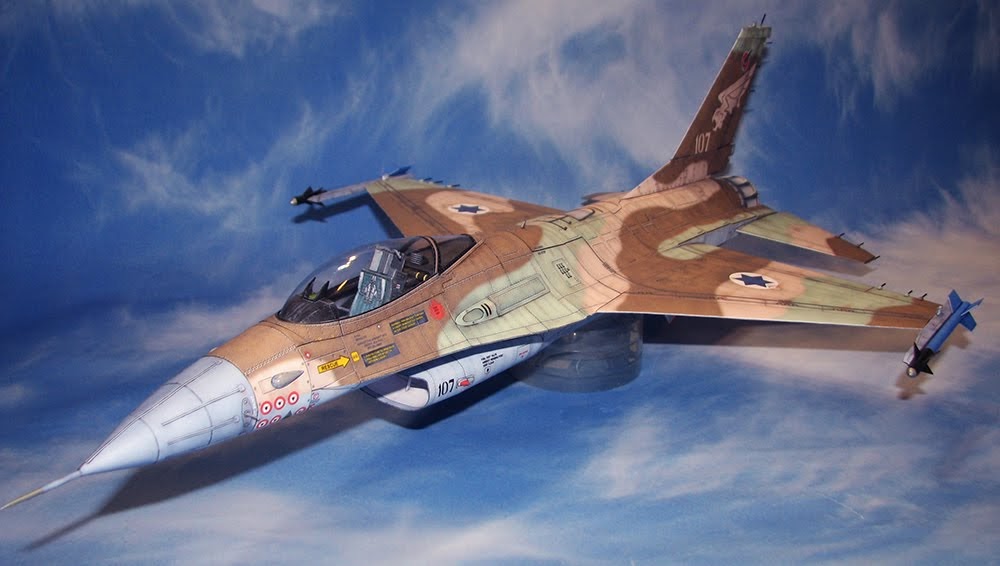

- Resources
- Received from the internet.
- Author
- Yoav Hozmi
- Printed File Format
- JPG
- Page(s)
- 20
- Instruction Format
- Image
Sponsored:
Sponsored 2:
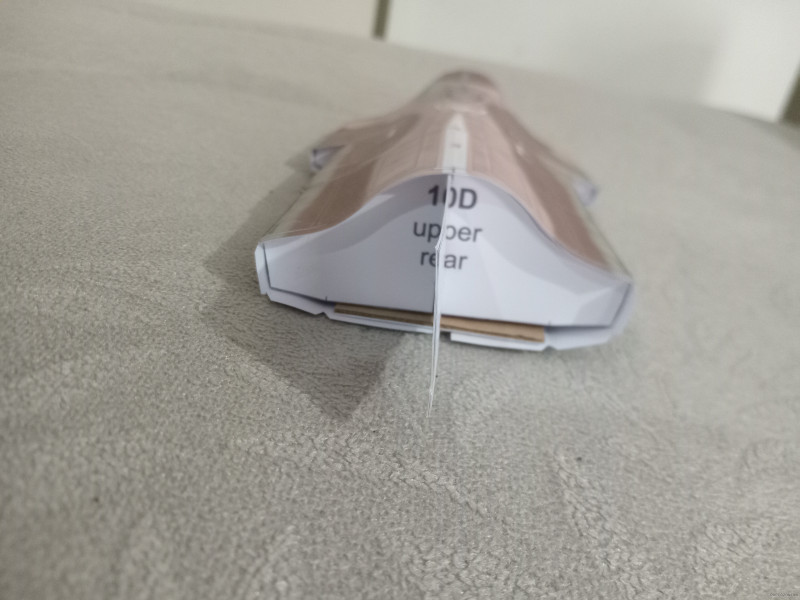
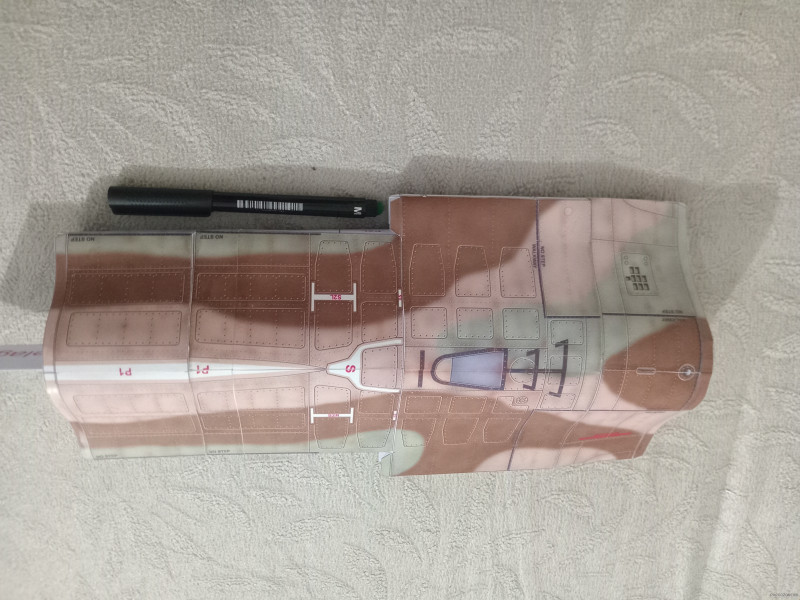
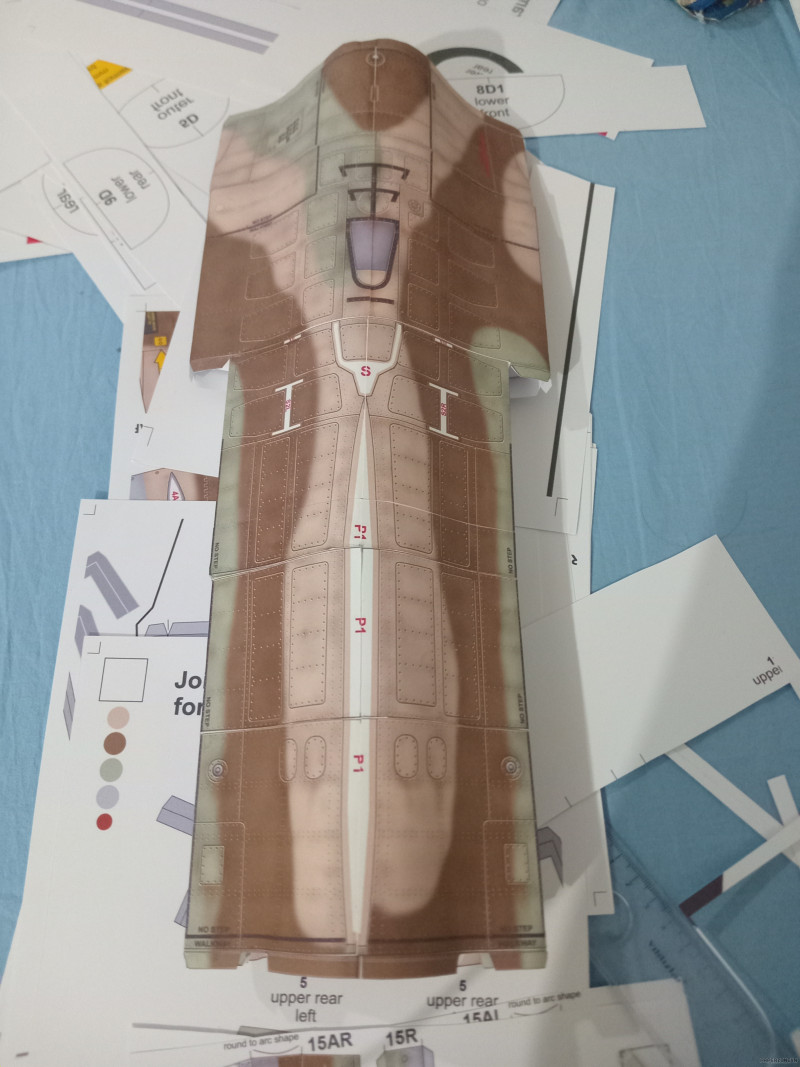
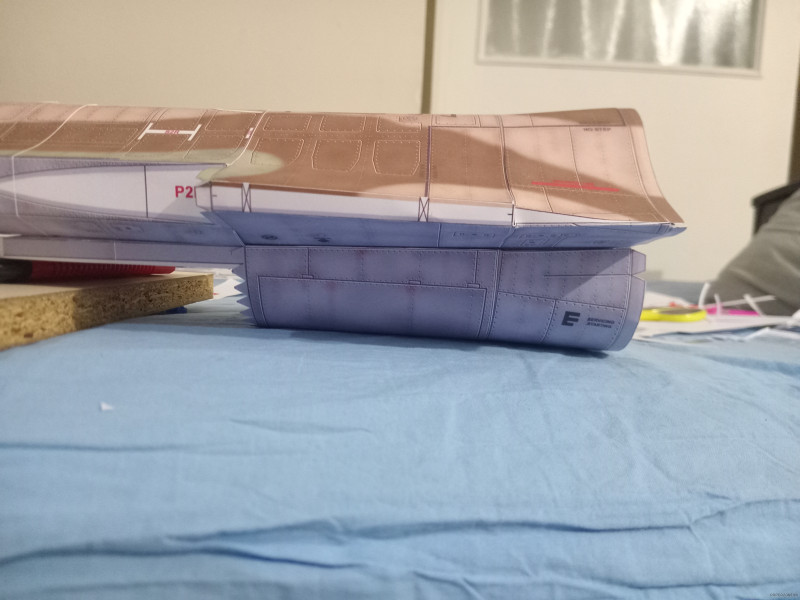
Jet Fighter F-16 Fighting Falcon Papercraft
To reflect this serious intent to procure a new fighter-bomber, the LWF program was rolled into a new Air Combat Fighter (ACF) competition in an announcement by U.S. Secretary of Defense James R. Schlesinger in April 1974. The ACF would not be a pure fighter, but multi-role, and Schlesinger made it clear that any ACF order would be in addition to the F-15, which extinguished opposition to the LWF.[28][29][30] ACF also raised the stakes for GD and Northrop because it brought in competitors intent on securing what was touted at the time as "the arms deal of the century".] These were Dassault-Breguet's proposed Mirage F1M-53, the Anglo-French SEPECAT Jaguar, and the proposed Saab 37E "Eurofighter". Northrop offered the P-530 Cobra, which was similar to the YF-17. The Jaguar and Cobra were dropped by the MFPG early on, leaving two European and the two U.S. candidates. On 11 September 1974, the U.S. Air Force confirmed plans to order the winning ACF design to equip five tactical fighter wings. Though computer modeling predicted a close contest, the YF-16 proved significantly quicker going from one maneuver to the next and was the unanimous choice of those pilots that flew both aircraft

To reflect this serious intent to procure a new fighter-bomber, the LWF program was rolled into a new Air Combat Fighter (ACF) competition in an announcement by U.S. Secretary of Defense James R. Schlesinger in April 1974. The ACF would not be a pure fighter, but multi-role, and Schlesinger made it clear that any ACF order would be in addition to the F-15, which extinguished opposition to the LWF.[28][29][30] ACF also raised the stakes for GD and Northrop because it brought in competitors intent on securing what was touted at the time as "the arms deal of the century".] These were Dassault-Breguet's proposed Mirage F1M-53, the Anglo-French SEPECAT Jaguar, and the proposed Saab 37E "Eurofighter". Northrop offered the P-530 Cobra, which was similar to the YF-17. The Jaguar and Cobra were dropped by the MFPG early on, leaving two European and the two U.S. candidates. On 11 September 1974, the U.S. Air Force confirmed plans to order the winning ACF design to equip five tactical fighter wings. Though computer modeling predicted a close contest, the YF-16 proved significantly quicker going from one maneuver to the next and was the unanimous choice of those pilots that flew both aircraft

Sponsored: Google Advertising