- Thumbnail
-

- Resources
- www.l-paper.com/
- Author
- L-paper
- Printed File Format
- PDO
- Page(s)
- 7
- Part(s)
- 99
- Instruction Format
- PDO
Sponsored:
Sponsored 2:
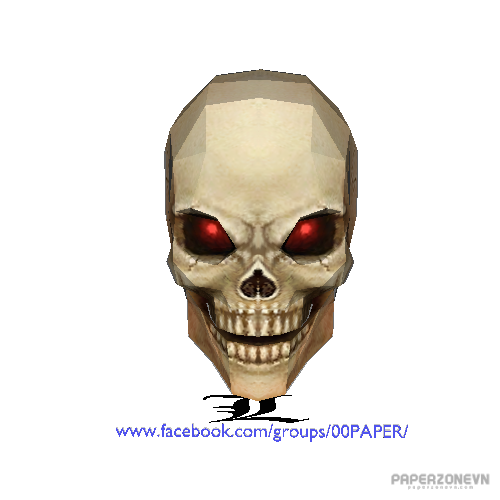
Human Skull Red Eyes

Functions of the skull include protection of the brain, fixing the distance between the eyes to allow stereoscopic vision, and fixing the position of the ears to enable sound localisation of the direction and distance of sounds. In some animals, such as horned ungulates (mammals with hooves), the skull also has a defensive function by providing the mount (on the frontal bone) for the horns.
The English word skull is probably derived from Old Norse skulle,[4] while the Latin word cranium comes from the Greek root κρανίον (kranion). The human skull fully develops two years after birth.The junctions of the skull bones are joined together by structures called sutures.
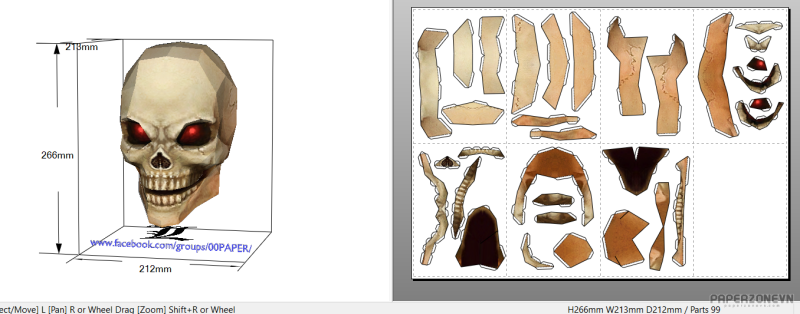

Functions of the skull include protection of the brain, fixing the distance between the eyes to allow stereoscopic vision, and fixing the position of the ears to enable sound localisation of the direction and distance of sounds. In some animals, such as horned ungulates (mammals with hooves), the skull also has a defensive function by providing the mount (on the frontal bone) for the horns.
The English word skull is probably derived from Old Norse skulle,[4] while the Latin word cranium comes from the Greek root κρανίον (kranion). The human skull fully develops two years after birth.The junctions of the skull bones are joined together by structures called sutures.

Sponsored: Google Advertising
